
A significant association between scores on the DST and the Cantonese version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (CMMSE) was found in this study (p < 0.05 for DSF, p = 0.00 for DSB).ĭementia and delirium were prevalent, yet under-recognized, in acute medical geriatric inpatients. Regarding the detection of major cognitive impairment, the ROC curve of DSB showed a sensitivity of 0.77 and specificity of 0.78 at the optimal cutoff of <3. The prior case-note documentation rate was 13.2% for dementia and 2.8% for delirium. Reversed is the opposite of forward, e.g.
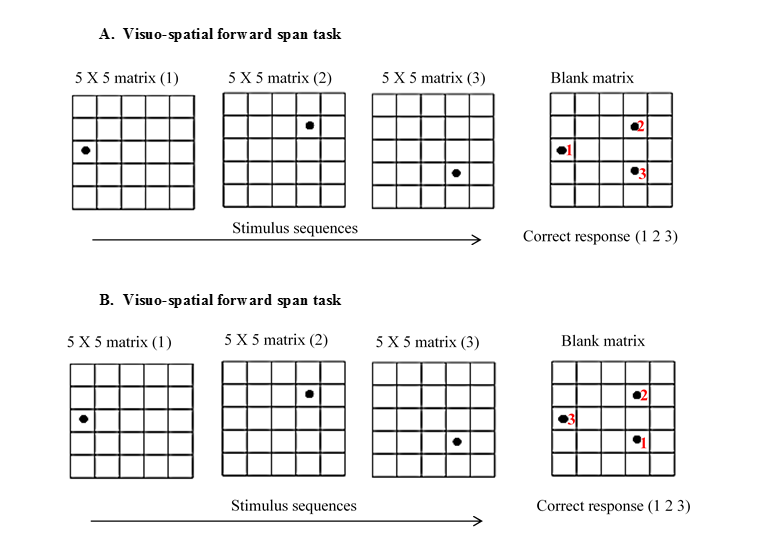
#Forward digit span test series
The first series is three numbers, such as '3, 9, 2. The person is then told to listen carefully because you will say a series of numbers and ask him to repeat them back to you in the same order you say them. the order in which the symbols must be entered, changes: Forward (default) requires the symbols to be entered in the order in which they were shown. The digit span test consists of telling the person that you are going to give him a short test. This is a verbal task, with stimuli presented auditorily, and responses spoken by the participant and scored automatically by the software. The prevalence rates of dementia alone, delirium alone and delirium superimposed on dementia were 21.5%, 9% and 9% respectively. Settings Test mode Depending on the selected mode, the target order, i.e. Digit Span (DGS) is a measure of verbal short term and working memory that can be used in two formats, Forward Digit Span and Reverse Digit Span. The test consists of two parts: repeating digit sequences in the order presented (forward digit span or FDS) or backward in reverse order (backward digit span or BDS). Receiver Operating Characteristics curve (ROC) was used in conjunction with sensitivity and specificity measures to assess the performance of DST. First, we identified the incidence of digit span impairments in a sample of 816 stroke survivors (541 males/275 females age at stroke onset 56 13 years time post-stroke 4.4 5.2 years). The DST scores were compared with the psychiatrists' DSM-IV-based diagnoses. We assessed verbal short-term memory impairments using a forward digit span task from the Comprehensive Aphasia Test. The objectives of this study were to (1) validate the Digit Span Test (DST) in the identification and differentiation of dementia and delirium and (2) determine the prevalence of major cognitive impairment in elderly people in an acute medical unit.ĭuring the study period from January to February 2010, 144 patients aged 75 years or more who had had unplanned medical admissions were assessed by nurses, using the Digit Span Forwards (DSF) and the Digit Span Backwards (DSB) tests. There is no valid instrument currently in use at acute-care hospitals in Hong Kong to aid the detection of cognitive impairment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
